Why does the combination of carbon and water correctly describe carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are disassembled or broken down by a process called hydrolysis.
Chapter 6 Carbohydrates Che 120 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Textbook Libguides At Hostos Community College Library
A carbohydrate ˌ k ɑːr b oʊ ˈ h aɪ d r eɪ t is a biomolecule consisting of carbon C hydrogen H and oxygen O atoms usually with a hydrogenoxygen atom ratio of 21 as in water and thus with the empirical formula C m H 2 O n where m may or may not be different from nHowever not all carbohydrates conform to this precise stoichiometric definition eg uronic.
. But in the nutrition world theyre one of the most controversial topics. A large number of analytical techniques have been developed to measure the total concentration and type of carbohydrates present in foods see Food Analysis by Nielssen or Food Analysis by Pomeranz and Meloan for more details. Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes.
They are organic compounds organized in the form of aldehydes or ketones with multiple hydroxyl groups coming off the carbon chain. A Fat catabolism produces more reduced cofactors gram per gram. The reactions of the monosaccharides can be conveniently subdivided into those associated with the aldehyde or keto group and those associated with the hydroxyl groups.
The relative ease with which sugars containing a free or potentially free aldehyde or keto group can be oxidized to form products has been known for a considerable time and once was the. These can consist of 3-carbon moieties triose 4-carbon units tetrose 5-carbon moieties pentose and 6-carbon moieties hexose. Carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula CH 2 O n where n is the number of carbons in the molecule.
Properties structure and function of biological macromolecules. The definition of carbohydrates in chemistry is as follows. The carbohydrate content of a food can be determined by calculating the percent remaining.
Carbohydrates consist of carbon hydrogen and oxygen. The term carbohydrate is itself a combination of the hydrates of carbon. The most important molecule s in the world is are _____.
Optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones or substances which give these on hydrolysis are termed as. Carbohydrates are macronutrients and are one of the three main ways by which our body obtains its energy. This formula also explains the origin of the term carbohydrate.
What elements are present in the amino acids that were not present in carbohydrates. The word carbohydrate is derived from carbon and water hydrate. D Fat catabolism leads to the formation of thioesters.
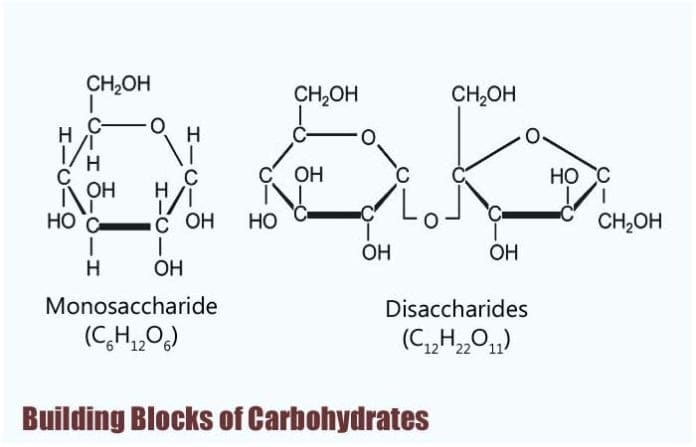
A single sugar unit is a monosaccharide. Carbohydrate molecules vary in size. The general empirical structure for carbohydrates is CH 2 O n.
The chemical formula of a carbohydrate is C x H 2 O y which denotes some carbons C with some water molecules H 2 O attachedhence the. Fructose A six-carbon monosaccharide consisting of hydroxyl groups in its cyclic form and a ketone group in its linear form. Monosaccharides disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Your body needs these macronutrients to stay healthy. B Carbohydrate catabolism involves substrate-level phosphorylation. The origin of the term carbohydrate is based on its components.
All carbohydrates are made from carbon hydrogen and oxygen. They are called carbohydrates as they comprise carbon hydrogen and oxygen at their chemical level. Molecular structure of triglycerides fats Saturated fats unsaturated fats and trans fats.
Why does the catabolism of fat produce more energy than an equivalent mass of carbohydrate. The presence of carbon makes carbohydrates organic rather than inorganic compounds. A more correct name used generally in Europe is glucides.
The word carbohydrate is derived from carbon and water hydrate. Why does this combination correctly describes this chemical group. A carbohydrate is a molecule made from carbon hydrogen and oxygen atoms and include a carbonyl group CO and a hydroxyl group -OH Carbohydrates are a main source of energy for most organisms and are also important as structural compounds and cell-cell recognition.
Carbohydrates are one of the four main molecules of life. Why does this combination correctly describes this chemical group. DNA takes the form of a double helix in which two antiparallel strands of nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds that form between the nucleobases.
In chemistry carbohydrates are a common class of simple organic compounds. The word carbohydrate comes from the Greek word sakharon which means sugar. They are also known as Saccharides which is a derivation of the Greek word Sakcharon meaning sugar.
Carbohydrates are essential nutrients which include sugars fibers and starches. Sugars starches and fiber are carbohydrates. They have twice as many hydrogen atoms as oxygen atoms.
Because the general formula of cabohydrates is Ca H2Ob. Other macronutrients include fat and protein. The components are carbon carbo and the components of water hence hydrate.
A six-carbon monosaccharide composed of hydroxyl groups in its cyclic form and an aldehyde group in its linear form. This is the currently selected item. Carbohydrates also called carbs are a type of macronutrient found in certain foods and drinks.
A carbohydrate is an aldehyde or a ketone that has additional hydroxyl groups. The building blocks of all carbohydrates are simple sugars called monosaccharides. There are two hydrogen bonds between each A-T pair and three hydrogen bonds between each G-C pair.
Hydrolysis is the breakdown of a chemical compound that involves splitting a bond by water. The term is easy to. Therefore the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 121 in carbohydrate molecules.
Biologically speaking carbohydrates are molecules that contain carbon hydrogen and oxygen atoms in specific ratios. The word carbohydrate is a combination of the names of these elements and means watered carbon. C Carbohydrate is catabolized anaerobically.
Carbohydrates are hydrates of carbon and have the generic structure of CnH2nOn. Carbon carbo and water hydrate. In solution the sugar exists mostly in its cyclic form and is the primary source of energy in the body.

Building Blocks Of Carbohydrates Types Properties Functions

Create A Concept Map Of Biomolecules Concept Map Biology Activity Graphic Organizers

0 Comments